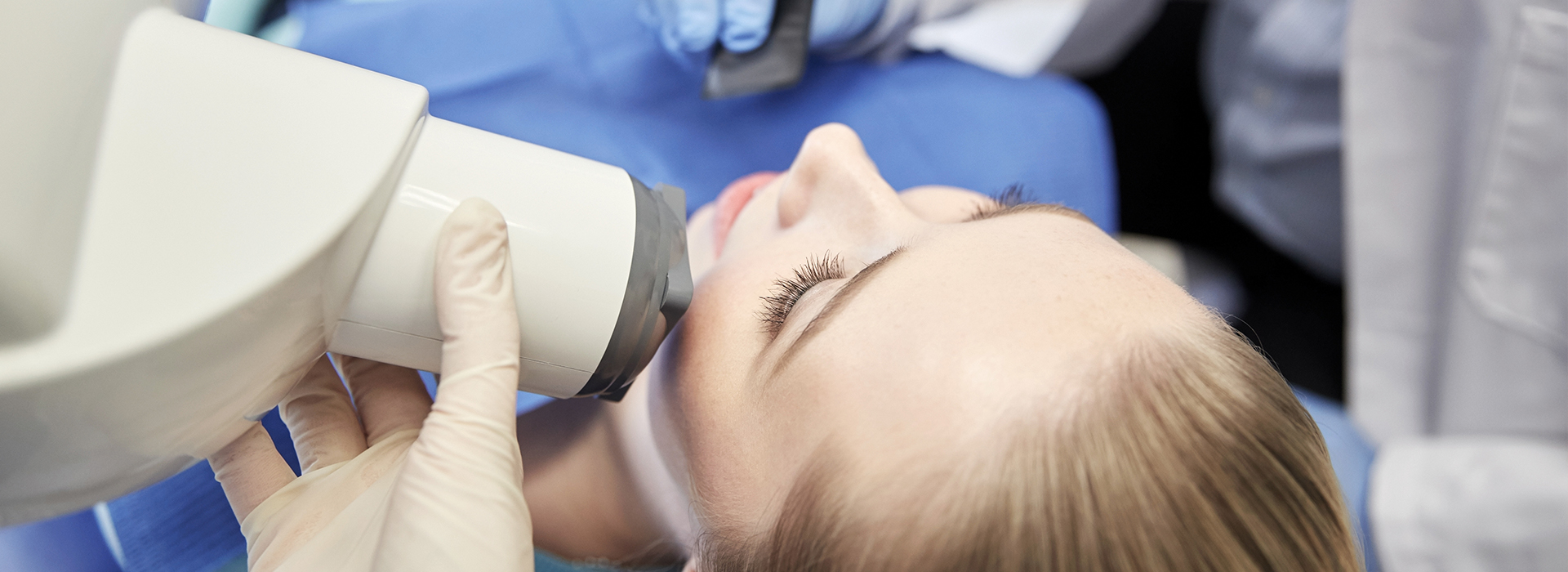
Digital radiography replaces traditional film with electronic sensors and computer software to capture dental images. Instead of holding film plates against the teeth, your dental team uses a slim sensor pad that records x-ray photons and converts them into a digital file. That file appears almost instantly on a monitor, where clinicians can view, enhance, and store it as part of your electronic health record.
The core components are the sensor, the x-ray source, and the imaging software. The sensor detects the x-rays that pass through teeth and surrounding tissues and sends a digital signal to the computer. Specialized software then renders that signal into a high-resolution image, often allowing adjustments to contrast, brightness, and zoom to highlight small details that might otherwise be overlooked.
Because the images are digital from the start, they integrate smoothly with modern practice workflows. Files are organized within the patient’s chart, can be included in treatment planning tools, and are easily referenced during visits. This streamlined process helps clinicians spend more time focusing on diagnosis and care and less time managing film and chemical development.
One of the most noticeable advantages of digital radiography is image clarity. Digital sensors capture subtle variations in density and structure, giving dentists a sharper, more detailed view of teeth, roots, and bone. Enhanced visualization can reveal early signs of decay, tiny fractures, or developing bone loss—information that supports more accurate clinical decisions.
Digital images can be manipulated without retaking x-rays: clinicians can adjust contrast, magnify specific areas, and apply filters that make diagnostic clues easier to see. These tools reduce the chance of missed conditions and often allow problems to be identified earlier, when treatment is simpler and outcomes are better.
Because images appear immediately, appointments move more efficiently. Instead of waiting for film to develop, your dental team can review results with you during the same visit, explain findings using on-screen images, and discuss recommended next steps. That immediacy helps patients understand their oral health and participate in care decisions with confidence.
Digital radiography requires significantly less radiation than traditional film x-rays because sensors are more sensitive to x-ray energy. This improved efficiency means less exposure is needed to capture an image of diagnostic quality. In practical terms, digital imaging delivers the information clinicians need while minimizing the dose to the patient.
Safety practices are still a priority: trained staff position sensors carefully, use shielding when appropriate, and follow accepted guidelines for when and how often images are taken. These safeguards, combined with the inherent efficiency of digital sensors, support a high standard of patient protection without compromising diagnostic effectiveness.
Beyond radiation dose, digital imaging is also more environmentally friendly. Eliminating film development removes the need for chemical processing and paper-based storage, reducing waste and chemical runoff. For practices aiming to reduce their environmental footprint, digital radiography is a responsible choice.
Digital files are easy to share securely with specialists, laboratories, or other providers when coordinated care is required. Rather than mailing or duplicating fragile film, clinicians can transfer encrypted image files quickly, enabling faster consultations and more coordinated treatment plans. This is particularly helpful for complex restorative or surgical cases that involve multiple providers.
Storing images electronically also strengthens record-keeping. Digital files are indexed within the patient’s chart, backed up by the practice’s data systems, and protected with access controls. That means images are less likely to be misplaced and can be retrieved instantly during follow-up visits, aiding continuity of care and accurate long-term monitoring.
Digital integration supports advanced treatment workflows as well. Images can be combined with intraoral scans, electronic treatment plans, and diagnostic tools to create a complete clinical picture. When used together, these technologies enable more predictable outcomes and a smoother patient experience from diagnosis through follow-up.
Undergoing digital radiography is straightforward and typically quick. During the procedure, a dental team member will place the small sensor inside your mouth in the area being examined and position the x-ray head outside your cheek. You may be asked to bite gently on a holder so the sensor stays steady while the image is captured.
Images appear on the computer within seconds. Your clinician will review them and may make on-screen adjustments to explain findings more clearly. Because images are immediate, your visit usually requires fewer steps: the team can review results and discuss recommendations without the need for a separate appointment to view film.
If you have questions about radiation exposure, how images are stored, or why a particular view is necessary, feel free to ask your dental team. Clear communication about the purpose and benefits of each image helps patients feel informed and reassured about their care.
In summary, digital radiography modernizes dental imaging by delivering clearer, faster, and safer diagnostic information while improving workflow and record-keeping. The practice’s adoption of this technology reflects a commitment to precise diagnosis and patient comfort. For more information about digital x-rays or how they are used in your care, please contact us to speak with a member of our team.

Digital radiography replaces traditional film with electronic sensors and imaging software to capture dental x-rays almost instantly. A small intraoral sensor or external detector records x-ray photons and converts them into a digital signal that the computer renders as a high-resolution image. Clinicians can then adjust brightness, contrast and magnification to highlight subtle details that may indicate decay, fractures or bone changes.
The core components are the x-ray source, the sensor and specialized software that stores images in the patient record. Because the image is digital from the start, files integrate with treatment-planning tools and electronic charts, which streamlines appointments and reduces handling of physical film. This efficiency helps the dental team focus on diagnosis and patient communication rather than on film development and storage.
Unlike film, digital sensors are more sensitive to x-ray energy and produce images instantly on a monitor instead of requiring chemical processing. Digital images offer superior dynamic range and can be enhanced with software tools to reveal fine diagnostic details that film can miss. The absence of film processing eliminates chemicals and paper records, which reduces environmental waste and simplifies record keeping.
Digital files are easier to organize, copy and transmit securely when coordination with other providers is needed, whereas film requires physical handling or scanning. The workflow improvements reduce appointment time and often decrease the need for repeat exposures because images can be reviewed and adjusted immediately. Overall, digital radiography provides faster, clearer results with fewer logistical steps than film systems.
Digital sensors are more efficient than film, so they require a smaller radiation dose to produce diagnostic-quality images. Modern digital radiography typically uses only a fraction of the radiation compared with older film techniques, and practices follow professional guidelines to limit exposures to what is clinically necessary. Staff use positioning aids, shielding and exposure protocols tailored to the patient to further minimize dose.
For most patients, the diagnostic benefits of digital x-rays outweigh the minimal radiation risk, particularly when images help detect problems early and guide conservative treatment. If you have specific concerns—such as pregnancy or a history of frequent imaging—discuss them with your clinician and they will adjust imaging protocols or postpone nonessential x-rays when appropriate. Open communication ensures images are taken only when the information will meaningfully affect care.
A digital radiography appointment is typically quick and straightforward: a team member places a small sensor in the area being examined while the x-ray head is positioned outside the cheek. You may be asked to bite gently on a holder to keep the sensor stable while the image is captured, and most exposures take only a second or two. Images appear on the computer monitor almost immediately for review by the clinician.
After the image is taken, your clinician can adjust contrast and zoom to point out findings and explain treatment options using the on-screen image. Because the images are available during the same visit, the team can usually discuss recommendations without scheduling a follow-up solely to review x-rays. If you have questions about the purpose of a particular view or the safety measures used, the team will explain them in plain language.
Digital x-rays provide higher resolution and better contrast than many film systems, allowing clinicians to detect early decay, small root fractures and subtle bone changes that might otherwise be missed. Software tools enable magnification, measurement and image enhancement, which support more precise diagnoses and clearer documentation of findings. Early detection often allows for less invasive treatment and better long-term outcomes.
Because images integrate with digital treatment-planning tools, clinicians can combine radiographs with intraoral scans and clinical photos to create comprehensive plans for restorative or surgical care. This digital integration improves predictability and helps the team communicate expected steps and timelines to patients. Clear visual information also helps patients understand the rationale for recommended procedures and participate actively in care decisions.
Digital radiographs can be shared quickly and securely with specialists, laboratories or referring providers when coordinated care is needed. Rather than sending physical film, practices transfer encrypted image files through secure clinical networks or protected patient portals, which speeds consultation and reduces the risk of lost records. Sharing digital images facilitates collaborative planning for complex restorative or surgical cases.
Patient privacy is protected by data security practices such as access controls, user authentication and encrypted transmission and storage. The practice stores images within the electronic health record under restricted access so only authorized team members can view them. If you have questions about how your images are shared or who can access them, ask the dental team for details on their privacy and security policies.
Digital radiographs are stored electronically in the patient’s record and indexed for quick retrieval during follow-up visits. Files are typically backed up by the practice’s data systems to prevent accidental loss and to support continuity of care over time. Storing images digitally reduces physical storage needs and makes it easy to compare current images with prior records during ongoing treatment or monitoring.
Retention periods vary by clinical need and legal requirements, but practices keep radiographs long enough to support ongoing dental care and meet regulatory standards. Digital storage also facilitates secure transfer if you change providers or need a second opinion. If you want to know how long your images will be retained or how to obtain a copy, the dental team can explain the practice’s record-retention policy.
Digital radiography can be appropriate for children and pregnant patients when images are clinically necessary and performed with appropriate safety measures. For children, sensors and exposure settings are adjusted for smaller anatomy and lower dose, and the team follows pediatric imaging guidelines to limit exposures. The decision to image a pregnant patient is made conservatively; nonurgent x-rays are often postponed until after delivery, while essential imaging is performed with abdominal shielding and strict dose control.
Clinicians weigh the diagnostic value of each image against any potential risk and follow accepted standards for timing and frequency of radiography. If you are pregnant or have concerns about imaging for a child, discuss them with the dental team so they can tailor the approach and explain why a given image is recommended or deferred. Clear discussion helps ensure imaging is used only when it will meaningfully inform care.
Digital radiographs integrate seamlessly with intraoral scanners, CBCT systems and treatment-planning software to create a multi-modal clinical record. Combining modalities lets clinicians correlate surface scans with internal anatomy, improving precision for implant placement, complex restorations and orthodontic planning. When images and scans are linked, the team can simulate outcomes and make more predictable treatment decisions.
This interoperability also enhances patient education by allowing clinicians to present combined visuals that explain conditions and proposed procedures. Digital integration reduces redundant imaging and enables efficient workflows across diagnostic, restorative and surgical disciplines. The result is a more coordinated patient experience from diagnosis through treatment and follow-up.
Tiger Family Dental uses digital radiography to deliver faster, clearer diagnostic information while minimizing radiation exposure and streamlining patient visits. The technology supports precise diagnosis, better treatment planning and immediate visual communication with patients, which aligns with the practice’s focus on modern, patient-centered care. Using digital imaging also reduces environmental waste associated with film processing and simplifies secure record-keeping.
Adopting digital workflows helps the team coordinate care more efficiently with specialists and laboratories and supports integration with other technologies used in comprehensive treatment. If you would like to learn how digital x-rays will be used in your care or to review a recent image, the clinical team at the practice will explain the findings and answer any questions you have. Clear communication ensures imaging is used thoughtfully to support your oral health goals.

Looking to schedule your next dental visit or learn more about our services?
Getting in touch with Tiger Family Dental is simple! Our friendly team is ready to help you book appointments, answer questions about treatments, and address any concerns. Whether you’d like to call, or use our convenient online form, we’re here to assist you. Take the first step toward a healthy, confident smile — contact us today and experience the difference personalized dental care can make.